© Copyright – 2010-2023 : All Rights Reserved. Sitemap
Power Distribution Unit PDU, rack mount PDU, PDU data center, Smart PDu, intelligent PDU
Power Distribution Unit PDU, rack mount PDU, PDU data center, Smart PDu, intelligent PDU
DTI-CX 2025 Digital Transformation Indonesia Conference, DATE:6-7 AUG.2025, Booth No.: C21
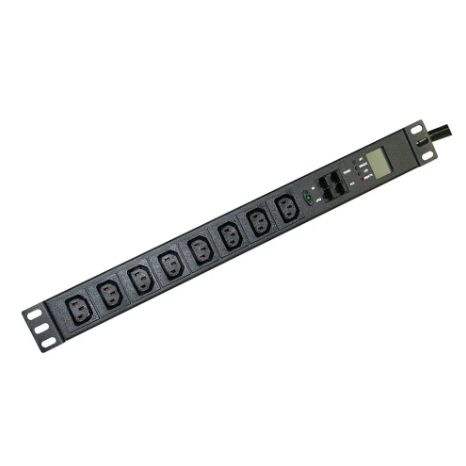

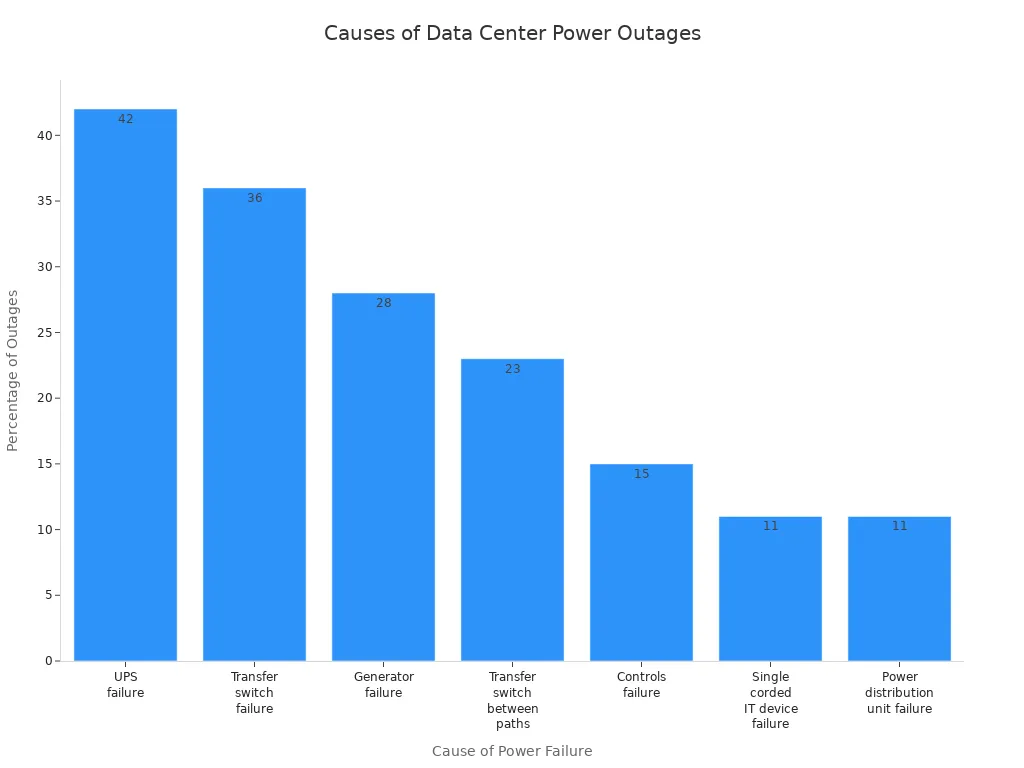
Selecting the right redundant pdu protects your equipment from unexpected downtime and financial loss. Power distribution unit failures account for 11% of data center outages, as shown below:
You need to focus on key factors to buying a pdu, such as power capacity, redundancy, and monitoring. A pdu buying guide helps you match these features to your needs, ensuring reliable uptime and future growth. Reliable redundant pdu choices support cost control and equipment safety.

You need to know how much power your equipment uses before choosing a redundant pdu. Start by making a list of every device in your rack. Check each device’s power rating on the manufacturer’s label or datasheet. For more accuracy, use a power monitoring tool to measure real usage. Multiply the current (amps) by the voltage (volts) to get the wattage for each device. For example, a server that draws 8 amps at 208 volts uses 1,664 watts.
Tip: Always add extra capacity for future growth. A good rule is to add 20% to your total power needs.
Here is a simple process you can follow:
You must match your equipment’s voltage and phase needs to your PDU. Most enterprise racks use 208V three-phase power. This setup supports both 208V and 120V outlets, which gives you flexibility for different devices. High-power servers often use IEC C-13 or C-19 outlets rated for 208V or 230V. Some data center needs require 400V three-phase PDUs, which provide 230V per circuit. Always check your equipment’s voltage and plug type before you buy.
Proper load balancing keeps your power system safe and reliable. Distribute your equipment’s power draw evenly across both PDUs. Use metered or smart PDUs to monitor loads in real time. Avoid running PDUs near their maximum capacity. Set alert thresholds lower for redundant systems to allow for failover. Train your team to manage dual-corded devices and check that each power supply connects to a different PDU. This practice helps prevent overloads and keeps your equipment running smoothly.
When you select a redundant PDU, you need to understand the difference between N+1 and 2N redundancy. These two models help you meet different redundancy requirements and affect your system’s reliability and cost. The table below shows a clear comparison:
| Redundancy Type | Configuration Description | System Capacity | Reliability Impact | Cost | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N+1 | N units plus 1 spare unit | Full load plus 1 spare unit | Can handle a single component failure, moderate reliability | Moderate cost | Small to medium data centers, critical HVAC systems |
| 2N | Two independent sets of N units, each capable of full load | Full load in each independent system | Handles multiple failures, allows maintenance without downtime, higher reliability | High cost | Large data centers, hospitals, critical facilities |
N+1 redundancy gives you a spare unit to cover a single failure. 2N redundancy duplicates the entire system, so you can keep running even during maintenance or multiple failures. You should choose the model that matches your reliability goals and budget.
Redundancy in your power system is key to achieving high uptime. A redundant pdu with dual power inputs and automatic transfer switching keeps your equipment running even if one power source fails. You get reliable power delivery because the system can switch instantly to a backup. This setup also allows you to perform maintenance without shutting down your equipment. Features like load balancing, surge protection, and remote monitoring further reduce the risk of downtime. In mission-critical environments, these features help you meet strict uptime targets and protect your operations.
Note: Redundant PDUs provide backup power paths and failover capabilities, which are essential for continuous operation in data centers and other critical facilities.
You need to match your redundancy requirements to your business needs. Consider these factors when choosing the right fault tolerance level:
You should also ask yourself important questions, such as how long your system can run during a failure and what happens if a component fails unexpectedly. Regular testing and maintenance ensure your redundancy plan works when you need it most. By balancing these factors, you can select a fault tolerance level that supports your operational goals and keeps your power system reliable.
You need to match the outlet types and quantity on your PDU to your equipment’s power needs. Each device in your rack may require a specific outlet, such as IEC C13, C19, or NEMA 5-15R. Choosing the right combination ensures every device connects safely and efficiently.
Modern PDUs often feature modular designs. You can add power modules or outlets as your requirements change. This flexibility helps you scale operations smoothly.
Tip: Always check your equipment’s plug type and power rating before choosing a PDU. This step prevents compatibility issues and ensures safe operation.
Plug compatibility is critical for seamless integration. You must ensure that your equipment’s plugs match the PDU’s outlets. Common plug types include IEC C13, IEC C19, and various NEMA standards. Matching these types prevents connection problems and supports reliable power delivery.
Proper cable management is also important. Organize cords to avoid tangling and maintain easy access for maintenance. Modular and scalable PDU designs can help you manage cables and fit your existing infrastructure.
Note: Always verify that the PDU’s input and output connectors align with your equipment’s plugs. This step ensures safe and reliable operation.
You have two main mounting options for PDUs: horizontal and vertical. Each option offers unique benefits and considerations.
| Mounting Option | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Vertical | Frees up rack space for servers and equipment; does not use rack units (0U); ideal for high-density racks | Limited to two per rack; requires enough rack width and depth; must be mounted at the back of the rack |
| Horizontal | Fits neatly inside the rack; flexible installation; useful when cabinet depth or cable management is a concern | Uses valuable rack space that could hold equipment |
Vertical mounting works well when you want to maximize rack space for IT equipment. You mount the PDU along the side or rear of the cabinet, keeping the center open for servers. However, you need to ensure your rack has enough space and that the PDU does not block access to the back of your devices.
Horizontal mounting fits inside the rack and can be more flexible, especially if you have unique cable management needs. The trade-off is that it takes up rack units that you might otherwise use for equipment.
Plan your installation carefully. Consider power redundancy, phase balancing, and ease of maintenance when choosing a mounting option. Good planning helps you maintain uptime and simplifies future upgrades.
Choosing the right cord length and practicing effective cable management play a crucial role in maintaining a reliable and efficient data center environment. When you select cords for your redundant PDUs, always consider the shortest length that allows safe and secure connections. Shorter cords help you minimize clutter and reduce the risk of airflow obstruction inside your racks.
Proper cable management keeps your equipment cool and easy to maintain. If you let cables hang loosely or use cords that are too long, you create obstacles that block airflow. This can cause your servers to overheat and force cooling fans to work harder, which increases energy consumption. You should always plan your cable lengths and routing before installation. This step helps you avoid blocking hot exhaust air paths and keeps hot and cold aisles separated, which is essential for cooling efficiency.
You can follow these best practices to improve cable management in your racks:
Tip: Avoid excess slack in your cords. Extra cable length not only clutters your rack but also increases the chance of tangling and accidental disconnections.
When you plan your cable management strategy, you make maintenance tasks faster and safer. Technicians can quickly identify and replace cables without disturbing other connections. Good cable management also protects your investment by reducing wear and tear on cords and connectors. By keeping your racks tidy and your airflow unobstructed, you support the long-term reliability and performance of your redundant PDUs and all connected equipment.

You can choose from several types of power distribution units, each offering different features for your data center. Here is a quick overview:
| PDU Type | Functionality | Use Cases and Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Basic | Simple power distribution without monitoring or control features. | Suitable for small or budget-conscious environments needing straightforward power delivery. |
| Metered | Adds local real-time power consumption monitoring but no remote access. | Ideal for data centers and industrial sites requiring power usage insights and overload alerts. |
| Monitored | Enables remote real-time monitoring, historical data access, and alarm notifications. | Used in facilities needing remote visibility into power metrics and proactive management. |
| Switched | Combines monitoring with remote control of individual outlets, allowing remote power cycling. | Favored in dynamic environments requiring remote power management, rebooting, and load balancing. |
You should select the PDU type that matches your operational needs. Basic PDUs work well for simple setups. Metered and monitored PDUs help you track power use and prevent overloads. Switched PDUs give you the most control, letting you manage power remotely and respond quickly to issues.
Modern types of PDUs offer advanced monitoring and control features that help you maintain uptime and efficiency. You can track real-time power consumption at both the rack and outlet levels. This helps you spot energy waste and balance loads. Remote management lets you switch outlets on or off from anywhere, which speeds up maintenance and reduces downtime. Intelligent PDUs also provide automatic switching between power sources, ensuring continuous operation even if one source fails. Management interfaces display key metrics like voltage, current, and kilowatts, and send alerts when thresholds are exceeded. These features help you act fast to prevent overloads and keep your equipment safe.
Tip: Remote monitoring and control can improve your maintenance response times by up to 40%, making your data center more reliable and efficient.
Environmental sensors in redundant PDUs play a vital role in proactive maintenance. These sensors monitor temperature, humidity, and airflow inside your racks. Early alerts warn you about overheating, condensation, or airflow blockages before they cause equipment failure. Automated notifications and incident reporting allow you to respond quickly, reducing the risk of downtime. Remote monitoring means you can troubleshoot and power cycle equipment without visiting the site. Predictive analytics and AI-driven alerts help you schedule maintenance before problems occur. Facilities using these technologies often see faster response times and improved uptime.
Note: Integrating environmental sensors with your PDUs supports a safer, more reliable data center environment.
You need to protect your equipment from electrical surges and unexpected current spikes. Surge protection devices (SPDs) and the right breaker mechanisms play a key role in high-availability environments. Consider these recommendations:
Proper surge protection keeps your data center safe from voltage spikes. Install SPDs at distribution points like PDUs to shield sensitive equipment. Surge circuit breakers combine surge protection with circuit interruption, which enhances safety and extends equipment life. The table below summarizes best practices:
| Aspect | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Redundancy | Design power systems with redundancy to ensure uptime and avoid single points of failure. |
| Surge Protection | Use proper grounding and install SPDs to protect against electrical spikes. |
| Breaker Mechanisms | Select breakers capable of handling inrush current to prevent nuisance tripping. |
| Inrush Current Limiting | Employ technologies such as thermistors and soft-start devices to limit inrush current surges. |
| SPD Types | Utilize voltage-limiting, switching, or composite SPDs depending on application needs. |
| Installation Points | Install surge protectors at distribution points like PDUs to safeguard sensitive equipment. |
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) can disrupt your equipment and cause downtime. EMI filters in redundant PDUs block harmful interference and allow only safe currents to pass. You benefit from these features:
By filtering out EMI, you improve power quality and support reliable power distribution for your critical systems.
Selecting a trusted brand ensures long-term reliability and support for your power infrastructure. Brands like NBYOSUN meet international certifications such as ISO9001, UL, CE, and RoHS, which guarantee safety and quality. You should look for these features:
NBYOSUN’s proven performance, advanced monitoring, and strong client base make it a reliable choice for redundant PDUs in data centers and other mission-critical environments.
When you choose a redundant PDU, you should always look at the warranty and service options. These features protect your investment and help you avoid unexpected costs. Leading manufacturers like NBYOSUN, APC, and Eaton offer strong warranties that cover manufacturing defects and performance issues. You gain peace of mind knowing your equipment has protection from the start.
Warranties and service agreements do more than cover repairs. They also lower your total cost of ownership. Here is how they make a difference:
You should also consider the impact on your budget. The total cost of ownership includes more than the purchase price. It covers maintenance, energy use, and downtime. A good warranty and strong service support can save you money over time.
| Warranty/Service Feature | Benefit to You |
|---|---|
| Extended Warranty | Longer protection, fewer repair costs |
| Technical Support | Faster problem-solving, less downtime |
| Certifications (UL, ISO9001) | Assurance of quality and safety |
| Customization Options | Better fit for your unique requirements |
| Advanced Monitoring | Improved efficiency, lower operational costs |
Tip: Always check the warranty period and what it covers before you buy. Reliable service and support help you keep your data center running smoothly and protect your investment for years to come.
You need to make sure your redundant PDU fits your rack and supports efficient space use. Start by checking the rack’s physical dimensions and power ratings. This step helps you avoid blocking airflow or affecting device performance. Choose a mounting location on the rack’s side or back panel. This keeps cables organized and does not block cooling. Many professionals use 0U vertical PDUs to save valuable rack space. Before installation, sort and tag all cables. This makes future maintenance easier and keeps your setup neat.
Follow these steps for best results:
Tip: Avoid common mistakes like ignoring rack size, poor cable management, or skipping final checks.
You should size your redundant PDU to match both your current equipment and your UPS. First, list all devices and calculate their total power use. Make sure your UPS can handle peak demand and provide enough backup time. Choose a PDU with more capacity than you need now. This gives you room to add new devices later. Include at least 20% more outlets than your current device count. Modular PDUs let you expand or replace units as your data center needs change. Always match the PDU’s input to your power infrastructure and safety standards. Align the PDU’s capacity with your UPS to handle peak loads and backup requirements.
Note: Monitoring power use helps you spot trends and plan for future growth.
Dual-circuit PDUs give you extra protection by connecting to two independent power sources. This setup keeps your equipment running if one source fails. Automatic transfer switching lets the PDU switch between sources without manual help. You get better power management with features like load balancing, real-time monitoring, and remote control. These PDUs save space by combining two units into one chassis. This design also reduces cable clutter and electromagnetic interference. High-density PDUs support many devices in a small space, which is important for modern data center needs. Customizable options let you pick the right current, socket type, and cable length for your setup. Remember, you need to set up and monitor dual feeds carefully to get the most benefit.
Callout: Dual feed PDUs help you maintain uptime, support disaster recovery, and optimize rack space in high-density environments.
You can ensure your redundant PDU meets all technical and operational needs by following a clear process:
A pdu buying guide helps you match capacity, redundancy, and monitoring, supporting reliable and scalable power distribution.
A redundant PDU gives your equipment two separate power sources. If one source fails, the other keeps your devices running. This setup helps you avoid downtime and protects your critical systems.
Check your device’s power supply. If it has two power inputs, you can connect each to a different PDU. This feature is common in servers, network switches, and storage units.
Yes, you can install a redundant PDU in most standard racks. Measure your rack space and check mounting options. Make sure the PDU matches your equipment’s power and outlet needs.
You get real-time power data and remote control with monitored or switched PDUs. These features help you spot problems early, balance loads, and restart equipment without visiting the site.
Key Reasons Why Auto Transfer Switch PDUs Are Vital
Important Advantages Of Auto Transfer Switch PDUs Explained
A Professional And Leading Manufacturer
For OEM
& ODM Power Distribution Unit (PDU)
You Can Trust
CONTACT
Ningbo YOSUN Electric Technology Co., LTD
Leading Professional Manufacturer in PDU Power Solutions
Contact Info.